The Exchange Server database (EDB file) is the primary data repository used by Microsoft Exchange to store mailbox information. It is based on the Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) and organizes data using a B-tree structure for efficient indexing and retrieval.

An EDB file holds all essential mailbox content, including emails, drafts, sent items, calendar events, contacts, journals, notes, and more. However, EDB files are vulnerable to corruption due to various factors. When corruption occurs, it can lead to data inaccessibility and disrupt email communication across the organization.
1022 JET_errDiskIO Error : This occurs due to disk I/O failure, typically when the system cannot access the requested database page. It often results from incomplete transaction logs caused by database size restrictions.
1019 JET_errPageNotInitialized Error : This can occur when links between various database pages are invalid. It may also result from empty or uninitialized pages within the database.
1018 JET_errReadVerifyFailure Error : This error is caused by page-level corruption in the Exchange database. A checksum mismatch in the page header can also make the page unreadable.
1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch Error : This error occurs when one or more important files that are specified in the logs are missing, moved or altered with.
501 JET_errLogFileCorrupt and 510 JET_errLogWriteFail : These errors can result from log file corruption and failure to write to log files.
JET_errDatabaseDirtyShutdown : A Dirty Shutdown error in Microsoft Exchange Server occurs when the database fails to close properly, leaving it in an inconsistent state. This typically happens due to sudden power outages, server crashes, or insufficient disk space—resulting in uncommitted transaction logs. As a result, the database becomes unreadable, and users lose access to their mailboxes until the issue is resolved.
Steps to Resolve Dirty Shutdown error of Exchange database
How to Check the Exchange Mailbox for Corruption
To check the Exchange database (EDB) and mailboxes for corruption in Exchange 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019, launch the Eseutil.exe utility from the Exchange Server installation directory and run the command:
eseutil /mh
This will show whether the database is in a Clean Shutdown or Dirty Shutdown state.
- Clean Shutdown means the database is free from errors.
- Dirty Shutdown means the EDB file is corrupted or inconsistent with the transaction log files, and database recovery is required.
How to Repair an EDB File and Migrate to Live Exchange Server?
All the errors mentioned above can result in the Exchange database (EDB file) becoming corrupted, dismounted, or completely unmountable, making the mailbox data inaccessible. In such cases, manual recovery methods are often complex and limited — especially for Public Folders or severely corrupted databases.
This is where the EdbMails EDB Repair Tool offers a comprehensive solution. It enables you to repair offline, corrupted, or dirty shutdown EDB files and seamlessly migrate the recovered data to a Live Exchange Server.
Why Use EdbMails EDB Repair Tool?
- Supports offline EDB files from all Exchange Server versions, including legacy versions.
- Repairs dismounted and inaccessible EDB files — even in a dirty shutdown state.
- Preserves folder structure, metadata, and Unicode content.
- Enables direct migration to Live Exchange and Office 365.
- Offers a granular preview of all mailbox items before migration.
- Simple user interface with no PowerShell or technical expertise required.
Simple Steps to Repair and Migrate EDB Files Using EdbMails
- Download and install the EdbMails application on your Windows OS.
- Choose the EDB to PST / Exchange / Office 365 option from the main interface.
- Browse and select the corrupted EDB file you want to repair — this can include dirty shutdown EDB files, or legacy files such as priv1.edb and pub1.edb. For older Exchange versions (Exchange 2003 or below), make sure to include the corresponding .stm file, if applicable.
Once the recovery process begins, EdbMails will scan the corrupted EDB file and extract all recoverable data, including emails, contacts, calendars, tasks, notes, and other mailbox items. The duration of this process depends on the size of the EDB file and the extent of the corruption. During this time, the software performs a deep analysis to ensure that all accessible data is safely recovered. It’s recommended to let the process finish without interruption
Click on the ‘ + ’ icon to expand and select the mailbox or folder you wish to migrate to the Live Exchange Server.
Connect to your target live Exchange server with the necessary details
After a successful login, select the option to load the target Exchange server mailboxes
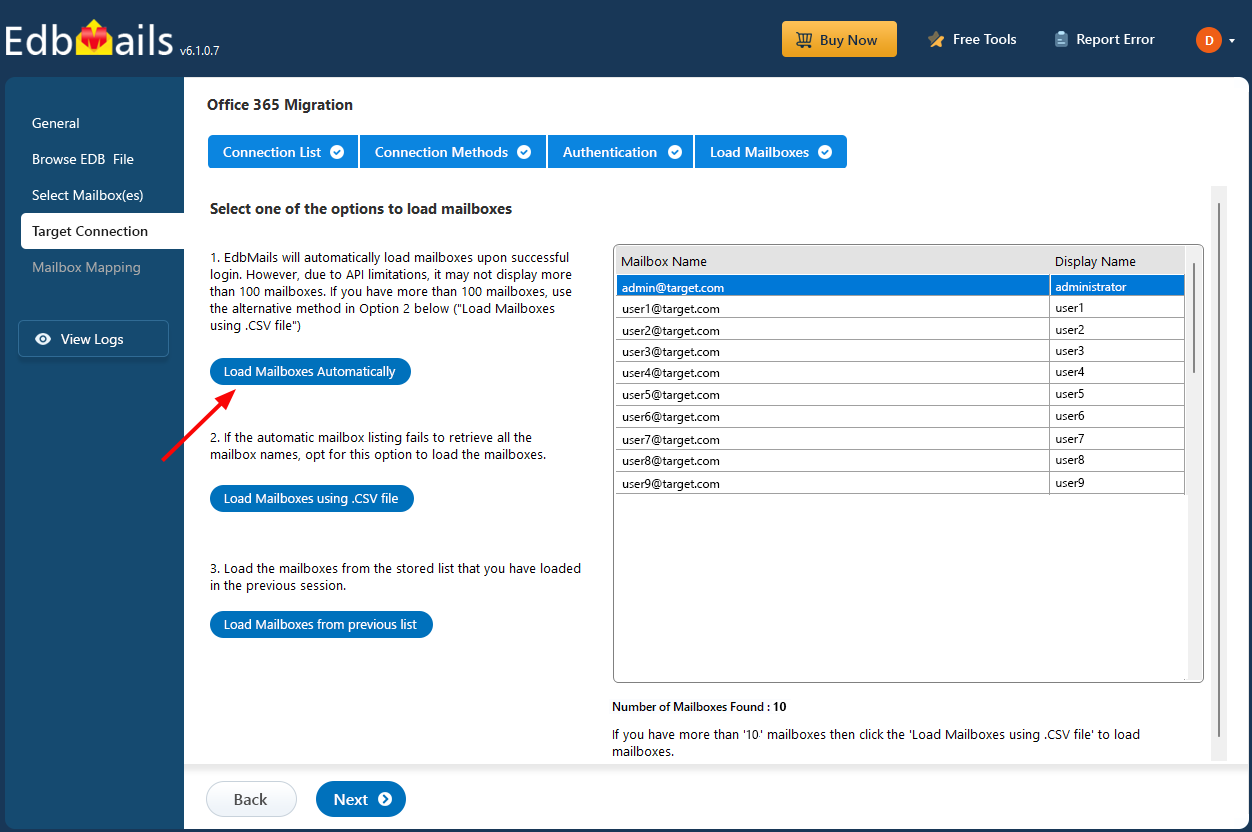
Choose the option to map the source mailboxes to the target live Exchange server mailboxes, then click ‘Start Migration’.
During the migration process, the progress will be displayed as shown in the screenshot below.
Once the migration operation is completed, the message ‘Migration operation has been completed.’ will be displayed.
Conclusion
EdbMails EDB Repair Tool is a reliable and efficient solution for fixing corrupted, dismounted, or inaccessible Exchange EDB files. It addresses various JET errors, supports all Exchange versions, and ensures complete recovery with data integrity. The tool simplifies the repair and migration process without requiring technical skills, making it ideal for organizations facing database corruption issues.