Managing mailboxes is a critical responsibility for every Exchange Server administrator. One common challenge is when a mailbox gets accidentally or unintentionally deleted. Fortunately, Microsoft Exchange Server provides built-in safeguards that prevent permanent deletion right away.
Instead of being erased instantly, deleted mailboxes are placed in a disabled state and retained in the database until the retention period expires. This allows admins to reconnect or recover them before they are purged.

In this article, we’ll cover:
- How Exchange mailbox deletion works
- How to modify mailbox retention settings
- Native methods to reconnect deleted mailboxes
- What to do when native recovery isn’t enough
- Why EdbMails Exchange Recovery Tool is the best solution for advanced scenarios.
How Exchange Server Handles Deleted Mailboxes?
When a mailbox is deleted in Exchange Server, it does not vanish immediately. Instead:
- It becomes disconnected (disabled) but remains in the mailbox database.
- By default, Exchange retains it for 30 days.
- After the retention period, it is purged permanently unless recovered.
This feature is a safety net for administrators, giving them time to restore critical mailboxes that may have been deleted by mistake.
Modifying Retention Policy
Administrators can customize the retention period to fit organizational needs:
- Right-click the Mailbox Store and select Properties.
- Open the Limits tab.
- Adjust the ‘Keep deleted mailboxes for’ value (number of days).
- Click OK to apply changes.
This flexibility ensures that organizations can balance storage efficiency with data recovery needs. For example, companies with strict compliance requirements may keep deleted mailboxes longer, while others may shorten retention to optimize storage.
Reconnecting Deleted Mailboxes via Exchange Admin Center
If the mailbox is still within the retention period, admins can easily reconnect it to a user account:
- Open Exchange Admin Center → Recipients → Mailboxes.
- Select More → Connect to Mailbox.
- View the list of disconnected mailboxes.
- If the mailbox doesn’t appear, run the Cleanup Agent to refresh the list.
- Select the mailbox and confirm reconnection.
- The mailbox is re-linked to its original user account.
Pro Tip:
- If the mailbox needs to be assigned to a new user, first create a user in Active Directory Users and Computers and then follow the above steps to connect it.
This method works well for straightforward scenarios but has limitations.
When Native Recovery Fails
There are situations where Exchange Admin Center cannot reconnect a mailbox:
- The EDB file is corrupted or inaccessible.
- The mailbox has been deleted beyond the retention period.
- The Exchange Server is dismounted or offline.
- The Active Directory user account is missing or inconsistent.
In these cases, relying on native tools alone may not be enough. This is where a specialized recovery solution becomes essential.
EdbMails: Complete Exchange Mailbox Recovery
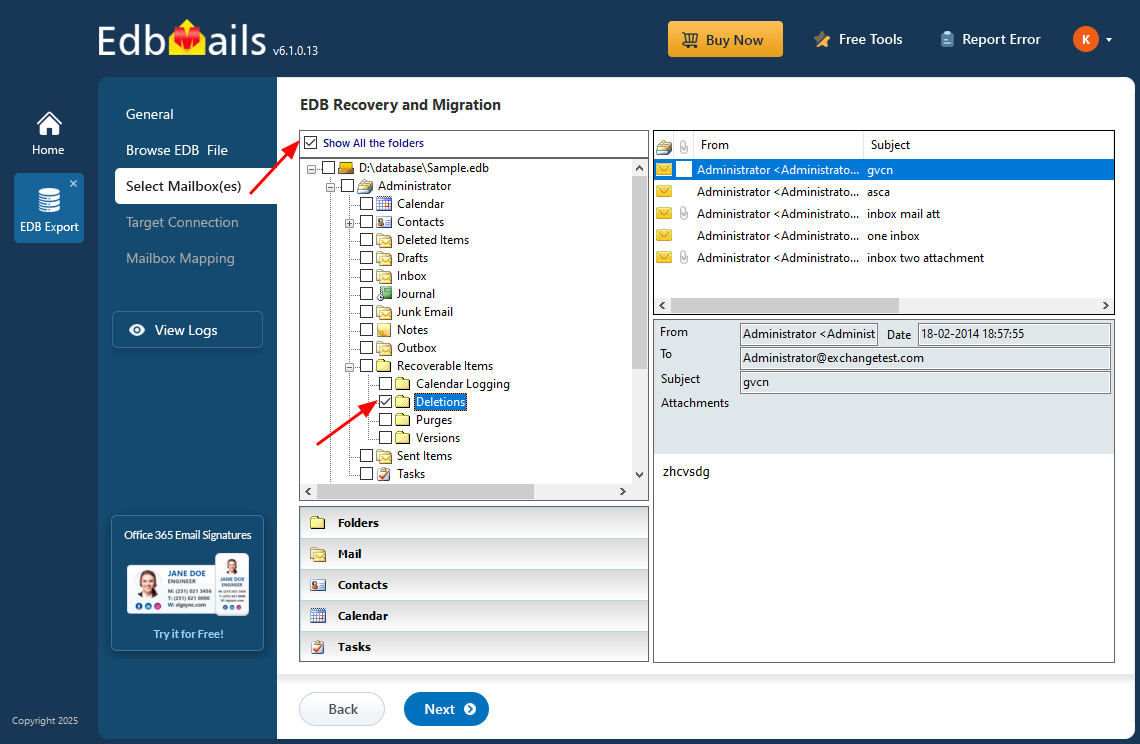
EdbMails Exchange Recovery Tool is designed to address complex mailbox recovery scenarios that Exchange native methods cannot handle.
Why Choose EdbMails?
- Deep Database Scanning
Recovers mailboxes even from severely corrupted or dismounted EDB files. - Full and Selective Export
Export entire mailboxes or by selecting specific folders (emails, contacts, calendars, tasks, notes). - PST Conversion Made Simple
Convert recovered mailboxes to Outlook PST format in just a few clicks. - Archive and Storage Optimization
Export inactive or departed employee mailboxes to PST and store them securely, freeing up Exchange server space. - Direct Migration Capabilities
Migrate mailboxes directly from EDB to Office 365 or Live Exchange without downtime. - Broad Compatibility
Supports all major Exchange versions (2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019) and works on both 32-bit and 64-bit Windows OS. - User-Friendly Interface
Designed for admins and IT teams, requiring no advanced technical expertise.
👉 For a detailed walkthrough, see our Step-by-Step Guide to Recover Deleted Exchange Mailboxes Using EdbMails.
Additional Benefits of EdbMails
- Split Large Mailboxes: Break down oversized mailboxes into smaller PST files.
- Support for Public Folders: Recover deleted items from Public Folder EDB files.
- Non-English Unicode Support: Full compatibility with international characters (French, Japanese, etc.).
- Advanced Filters: Export specific items by date, subject, or attachments.
- No Dependencies: Does not require Exchange services or Active Directory log files.
Conclusion
Recovering deleted mailboxes in Exchange Server is manageable when using built-in tools—provided the retention period has not expired and the database is healthy. However, in real-world scenarios where databases are corrupted, mailboxes are permanently deleted, or servers are offline, EdbMails Exchange Recovery Tool offers a robust and reliable solution.
By combining native Exchange capabilities with the advanced features of EdbMails, administrators can ensure zero data loss, efficient recovery, and business continuity.
👉 Try EdbMails Free Trial today and experience effortless mailbox recovery.
Exchange Mailbox Recovery : FAQs
1. Can I recover a mailbox after the retention period has expired?
Yes. Once the retention period ends, the mailbox is purged. Native recovery won’t work, but you can still recover it using EdbMails if the EDB file is available.
2. Do I need an active Exchange Server to use EdbMails?
No. EdbMails works with offline EDB files, even if the Exchange server is down or unavailable.
3. Can I recover specific items instead of the entire mailbox?
Yes. EdbMails supports granular recovery so you can export only emails, calendars, or specific folders.
4. Is there a size limit on the mailboxes EdbMails can recover?
No. EdbMails handles very large databases without any restrictions.
5. Does EdbMails support Exchange migrations as well?
Yes. You can directly migrate EDB mailboxes to Office 365 or Live Exchange with built-in mailbox mapping.



